|
| 1. Introduction |
|
|
| The altimeter settings procedures in use generally conform to those contained
in ICAO Doc 8168- OPS1611 Vol 1, Part 6 and are given in full below. |
|
|
| QNH reports and temperature information for use in determining adequate
terrain clearance is provided in MET broadcasts and is available on request from the Belize air
traffic service unit. QNH values are given in inches. Hectopascals (hPa) readings are available
on request. |
|
|
| 2. Basic altimeter setting procedures |
|
|
| 2.1 General |
|
|
| 2.1.1 The transition altitude for Belize is 19,500 ft. |
|
|
| 2.1.1.1 Vertical positioning of aircraft when at or below the transition
altitude is expressed in terms of altitude, where as such positioning at or above the
transition level is expressed in terms of flight levels. While passing through the transition
layer, vertical position is expressed in terms of altitudes when descending and in terms of
flight levels when ascending. |
|
|
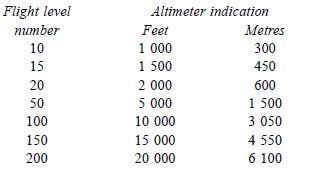
| 2.1.1.2 Flight Level Zero is located at the atmospheric pressure level of
29.92 inches (1013.2 hPa). Consecutive flight levels are separated by a pressure interval
corresponding 500 ft (152.4 m) in the standard atmosphere. |
|
|
| Note: Examples of the relationship between flight levels and altimeter
indications are given in the following table, the metric equivalent are being
approximate: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 2.1.2 Take-off and climb |
|
|
| 2.1.2.1 A QNH altimeter setting is made available to aircraft in taxi
clearance prior to take-off. |
|
|
| 2.1.2.2 Vertical positioning of an aircraft during climb is expressed in
terms of altitudes until reaching the transition altitude above which vertical positioning is
expressed in terms of Flight Levels. |
|
|
| 2.1.3 Vertical Separation – en route |
|
|
| 2.1.3.1 Vertical separation during en route flight shall be expressed in
terms of flight levels or altitudes during an IFR flight depending on the altitude or flight
level. as described in 2.1.2.2 |
|
|
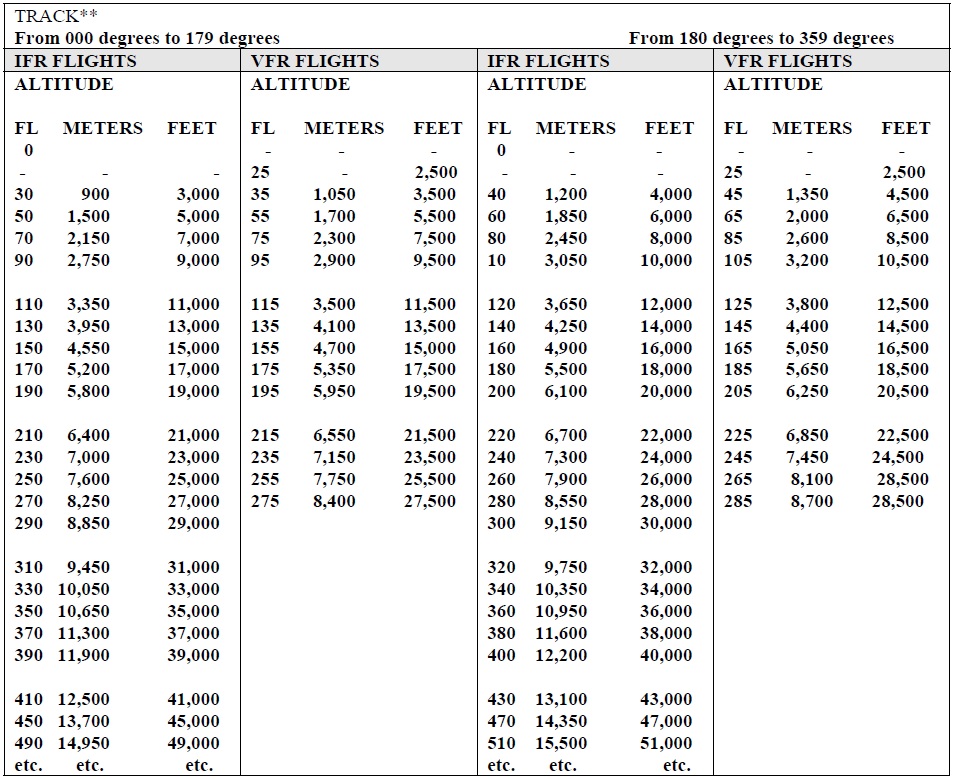
| 2.1.3.2 IFR flights, and VFR flights above 3,000 ft (900 m), when in level
cruising flight, shall be flown at such flight levels or altitudes, corresponding to magnetic
tracks shown in the following table, so as to provide the required terrain clearance: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Note: |
|
|
|
- Some of the lower levels in the above table may not be usable due to terrain
clearance.
- No VFR flight is permitted above
18,500ft.
- All levels from 3,000ft to 19,500ft are
expressed in altitudes.
- Above this, levels are expressed in
terms of flight levels. The first available flight level is FL200.
- An altitude of 2,500 may be utilized in
both cases.
|
|
|
| 2.1.4 Approach & Landing |
|
|
| 2.1.4.1 A QNH altimeter setting is made available in approach clearances and
in clearances to enter the traffic circuit. |
|
|
| 2.1.4.2 Vertical positioning if aircraft during approach is controlled by
reference to altitudes. |
|
|
| 2.1.5 Missed Approach |
|
|
| The relevant portions of 2.1, 2.2, 2.3, and 2.4 shall be applied to the case
of a Missed Approach. |
|
|
| 3. Description of altimeter setting region |
|
|
| Not applicable. |
|
|
| 4. Procedures applicable to operators (including
pilots) |
|
|
| 4.1 Flight Planning |
|
|
| The levels at which a flight is to be conducted shall be specified in a
flight plan: |
|
|
|
- in terms of flight levels if the flight is to be conducted above the transition
altitude, and
- in terms of altitudes if the flight is
to be conducted in the vicinity of an aerodrome, at or
- below the transition altitude
|
|
|
| Note: Flight levels are specified in a flight plan by number and not in terms
of feet or meters as is the case with altitudes. |
|
| 5. Tables of cruising levels |
|
|
| The cruising levels to be observed when so required are as follows: |
|
|
|
- in areas where, on the basis of regional air navigation agreement and in accordance with
conditions specified therein, a vertical separation minimum (VSM) of 2000ft is applied
between FL290 and FL410 inclusive:*
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|